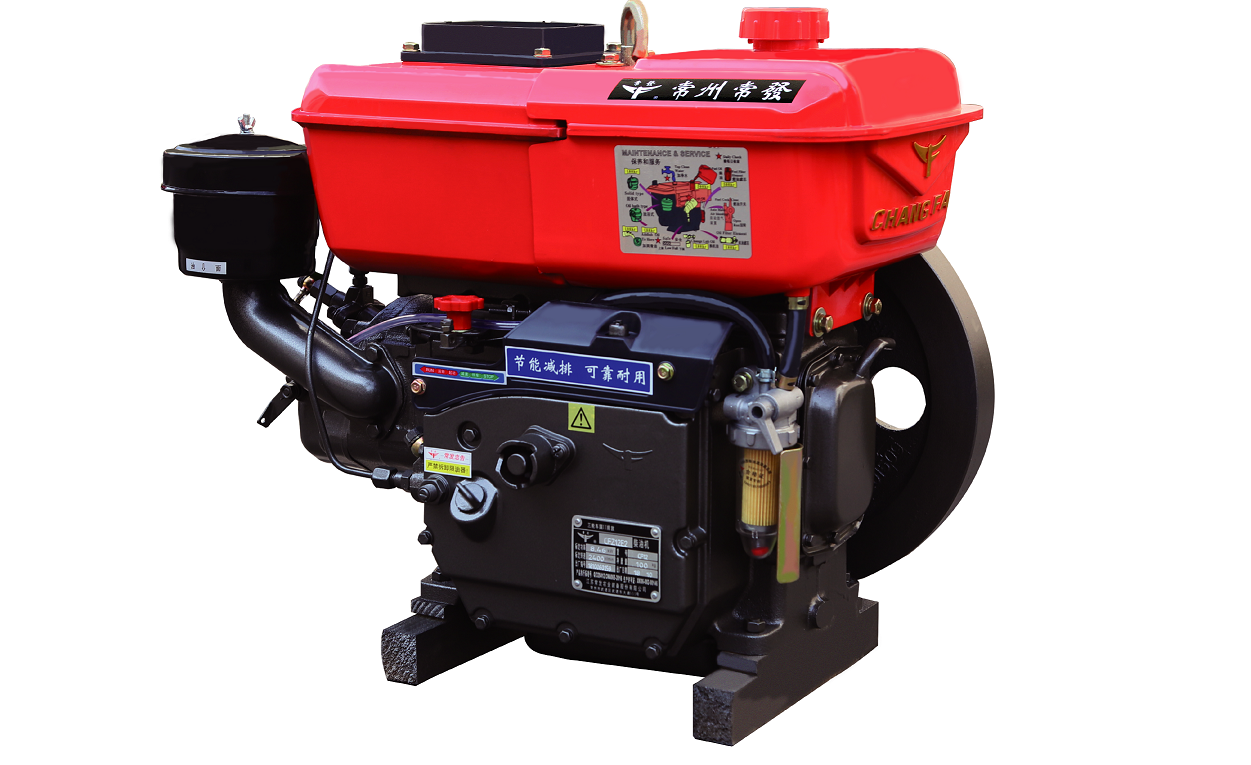
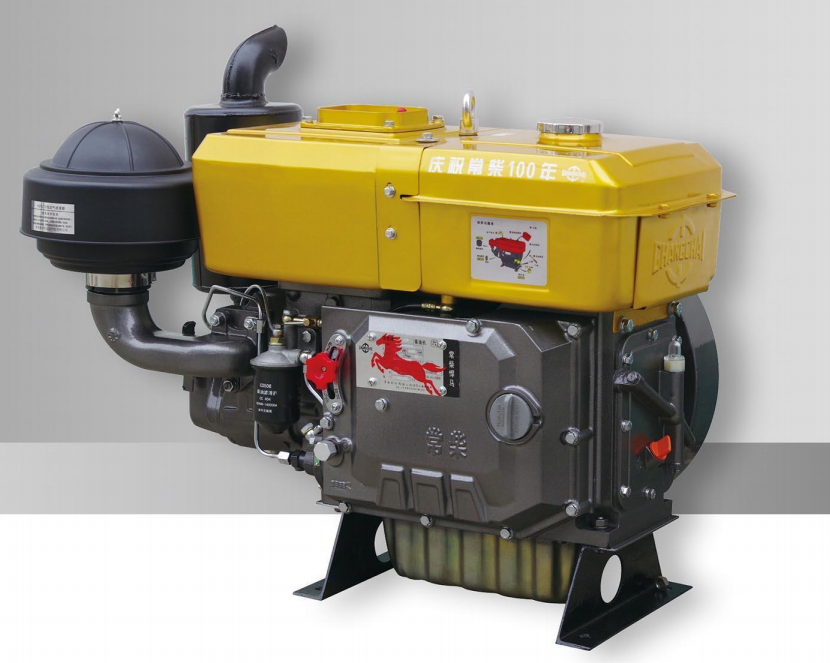
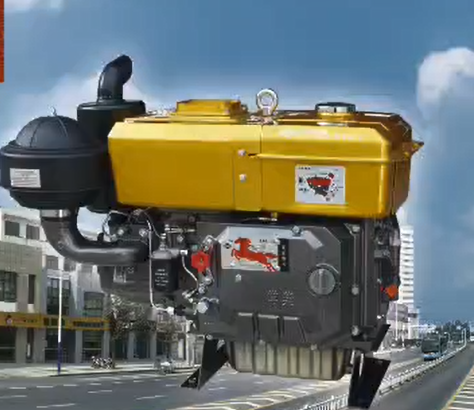
- What is an Engine?
An engine is a machine that takes energy from a source and converts it into mechanical work. It can be anything from a catapult or a trebuchet to a man-powered crane.
Most modern engines are internal combustion engines - they combust fuel in the presence of an oxidizer to release high-temperature, high-pressure gases that drive mechanical parts.
What is engine
- What is engine
An engine is a machine that uses energy, especially heat energy, to make a vehicle move. It also converts one form of energy into another, such as the burning of fuel to produce electricity.
The most familiar type of engine is the internal combustion (IC) engine that runs all modern automobiles. It is also a common source of power for many electric plants.
There are several different types of engines, and they all have unique features. But they all work in the same basic way.
To start, they all have pistons that pump inside of each cylinder and connect to and turn the crankshaft. The number of pistons that are pumped inside the cylinder at any given time is important to how well the engine performs.
These engines can be two-stroke or four-stroke. A two-stroke engine has pistons that move up and down inside the cylinder twice for every cycle of the crankshaft, which gives the engine more combustive events per rotation.
A four-stroke engine has pistons that move up, down, and sideways in each cylinder, giving the engine twice as many combustive events per rotation. This type of engine has a high average performance, but it uses more gas and oil.
- Type of engine
The engine is a machine that converts the energy of fuel into mechanical energy. It can be an internal combustion engine or an external combustion engine. It can also be a thermal engine that does not use the heat of combustion to generate mechanical energy.
Reciprocating engines: In a reciprocating engine the piston moves to and fro inside the cylinder. The pressure force generated by the burning of fuel is exerted on the piston and this pressure force is transmitted to the crankshaft through a connecting rod. This movement of the piston produces power. Reciprocating engines are classified into two stroke and four stroke engines.
Inline engines: This type of engine has the cylinders arranged in a straight line one behind the other along the length of the crankshaft. They are commonly used in automobiles and are a good choice for cars that need efficient fuel economy.
V-type engines: This is a popular layout on many cars and trucks. These are made up of a collection of 3, 4 or 6 cylinders on either side of the crankshaft.
Opposed cylinder engines: These are similar to V-type engines but have two cylinders banks opposite to each other. They are generally used in high-end vehicles and are very powerful.
Four stroke engines: This is a very common engine layout in automobiles and bikes. It is a very efficient engine design because it consists of two strokes in which the piston moves up from TDC to BDC and then back down from BDC to TDC.
- What are the uses of different types of engines
Engines convert a fuel (such as gasoline or diesel) into mechanical energy that produces motion. They can be used to power cars, locomotives or aircraft, and they are used in a variety of industrial processes as well.
There are many different types of engines. The most common are internal combustion engines. These can be two-stroke or four-stroke petrol or diesel engines.
An external combustion engine (EC engine) is a heat engine that uses an internal working fluid that is heated by combustion of an external source, through the engine wall or a heat exchanger. The internal working fluid expands and creates motion and usable work, and can then be cooled, compressed and reused (closed cycle), or dumped, and a cool fluid pulled in for use again.
EC engines are often confused with internal combustion (IC) engines, which also use a working fluid that undergoes thermal dilation-contraction or a shift in phase but whose chemical composition remains unaltered. Both systems combust fuel (or air) and oxidizer to produce energy.
IC engines are usually more efficient, but they also use a lot of fuel and emit pollutants. They can be made from many materials, but their most common components are pistons and cylinders. Some are reciprocating while others are rotary.

 中文
中文 English
English Español
Español Français
Français



