Hydraulic motors use a pressurized fluid to generate force and torque through a piston. This force is then transferred into linear movement through a cylinder.
This type of actuator is often used in heavy mobile equipment such as trucks and construction equipment. It is also useful for a wide range of applications that require precision positioning.
- What is hydraulic motor
A hydraulic motor is a type of mechanical actuator that converts pressure and flow from a hydraulic fluid into torque and angular displacement. These devices are used to drive various systems in the world, ranging from construction and mining equipment to agricultural machinery.
There are different types of hydraulic motors, and engineers must choose one that is appropriate for the application they need to use it in. The selection depends on the hydraulic system requirements, such as load, operating pressure, speed and serviceability.
Some of the common hydraulic motors are gear, piston and vane motors. Each of these motors has its own benefits and uses.
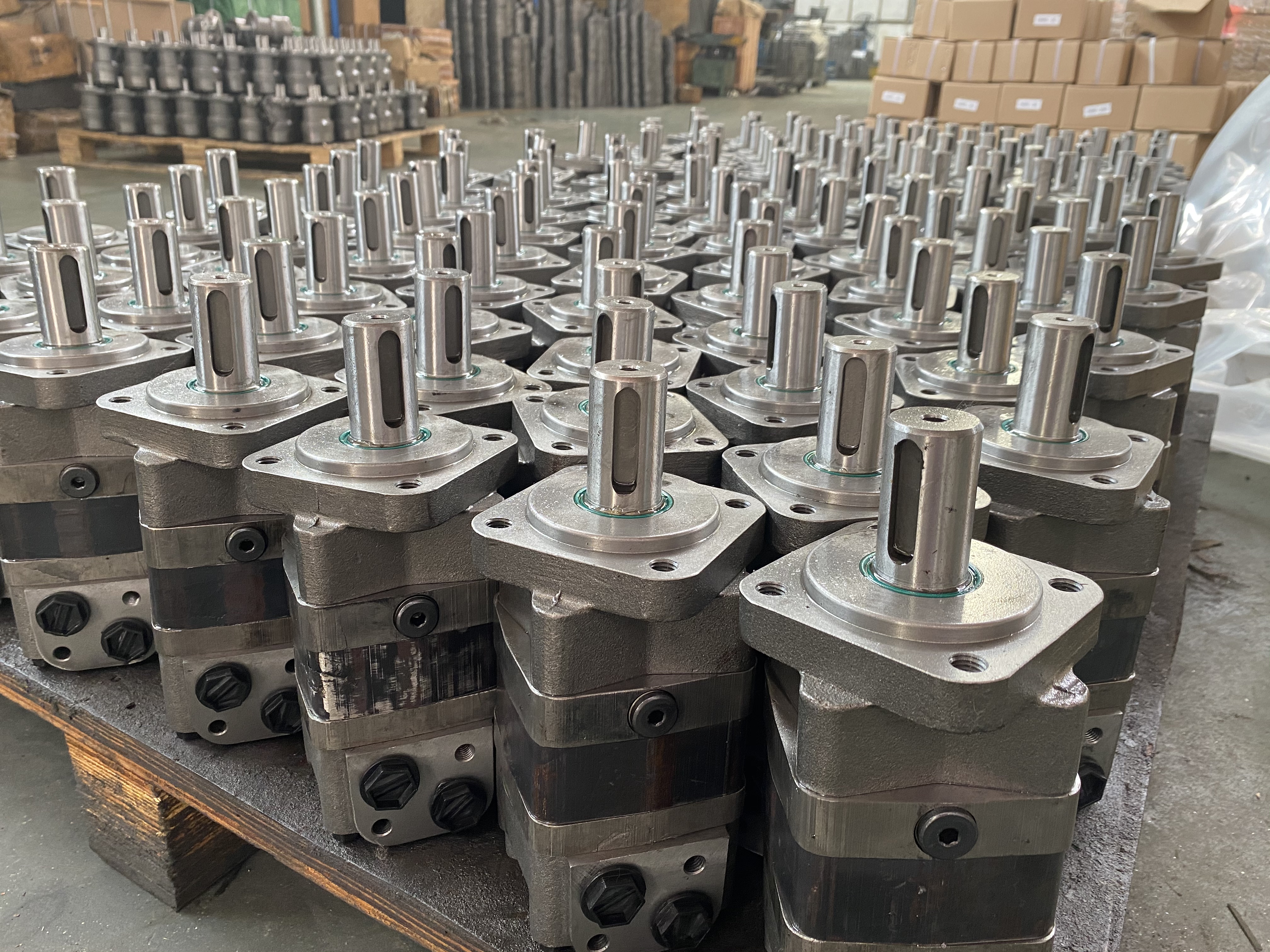
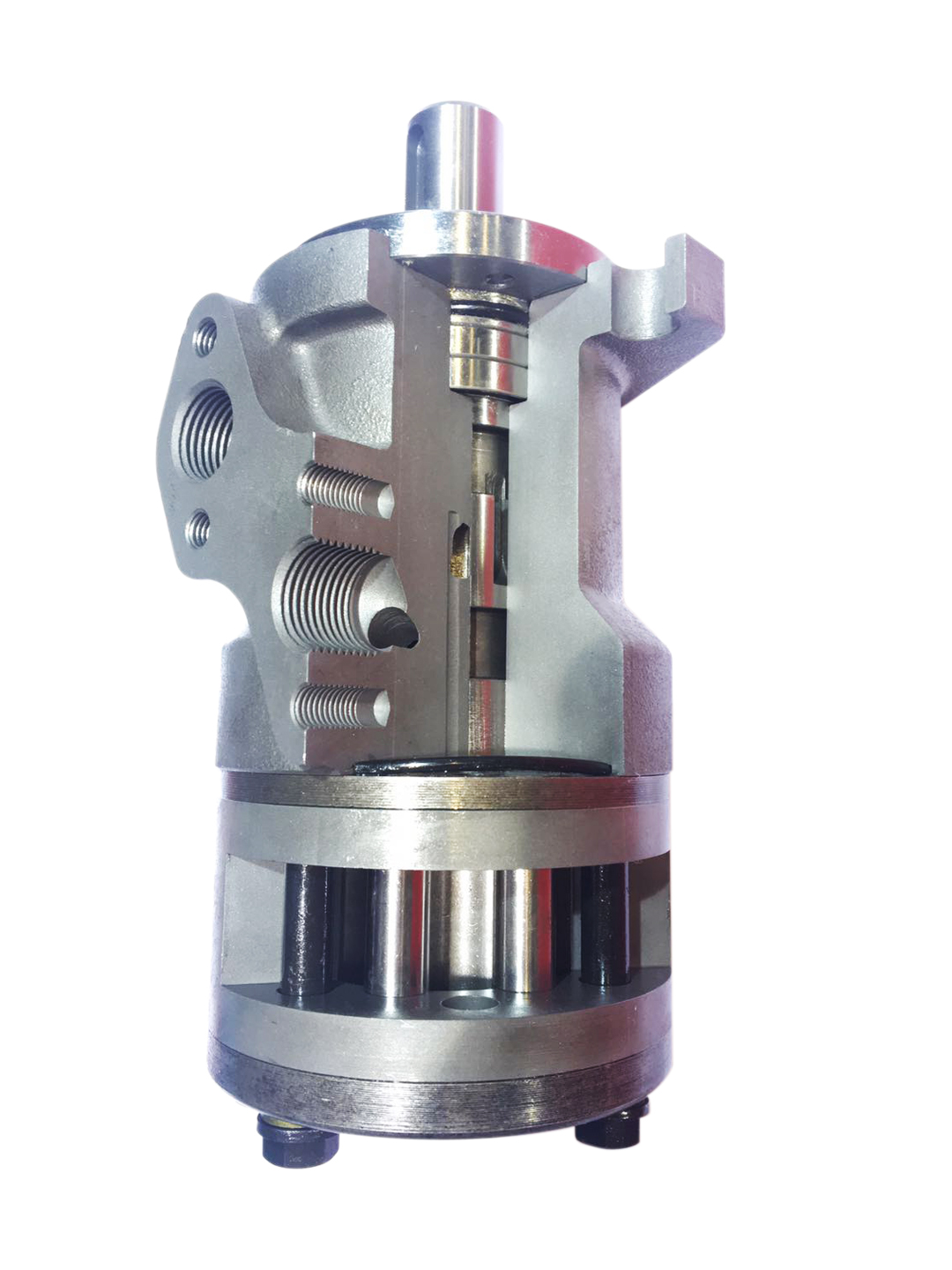
Gear motors are made up of two parts: an idler gear and a driven gear. They are attached to an output shaft. High-pressure oil is pumped into one side of the gears, then flows between the gear tips and the motor housing to an outlet port. The gears lock together, preventing the oil from the outlet side from flowing back into the inlet side.
The oil that is pumped into the gears also lubricates them. The motor also has a drain port that vents the oil out of the gears to clean them up. This reduces wear and tear on the gears and the main bushings..png)
.png)
- What is an electric motor
An electric motor is an electrically powered machine that converts electricity into rotation and other kinds of mechanical energy. It is a device that is widely used in cars, trains, power tools, fans, air conditioning, household appliances, disk drives, and even small electric watches.
A typical electric motor has two main parts, the rotor which is the part that moves and the stater which is the fixed part. The rotor usually holds conductors that carry current and the stator magnetic field applies a force on these conductors to spin the shaft of the rotor.
The windings that are used to carry the current will look familiar to anyone who has dealt with electrical components before. They are windings of wire that wrap around a metal core (magnet). The current passes through these windings and creates a magnetic field in the coiled wire.
Every type of wire has a weak magnetic field when it is coiled and the coiling creates a stronger magnetic field as the wire is turned. The number of coils on the rotor will determine the strength of this magnetic field and how smoothly it rotates.
The most common form of electric motor is the DC motor. These are 75-80% efficient, work well at variable speeds, and have great torque. They also are quiet and use a lot less energy than a standard AC fan. They can be shunt or series wound, are brushless or brushed, and run on a variety of DC or AC power supplies.
- Difference between hydraulic motor and electric motor
Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of a magnetic field and a winding current to produce force on the shaft. They are the most common type of motor in industrial applications.
Hydraulic motors convert pressure into torque and rotational energy by drawing fluid from a reservoir and pumping it through the motor’s cylinder. They are often used in combination with other hydraulic components, such as pumps and valves.
Depending on the flow, displacement and pressure drop in the cylinder, hydraulic motors can produce a wide range of power. They range in speed from low-speed units that operate at 0.5 rpm to high-speed models that can run up to 10,000 rpm.
Both types of motors can be used to move a variety of heavy loads. But electric motors are typically better suited to applications that require constant torque, such as those requiring continuous motion or that have multiple actuators working at once.
Both hydraulic and electric motors are designed to be reliable and efficient. However, hydraulic motors offer more versatility and cost-effectiveness when it comes to long-term operation and maintenance.

 中文
中文 English
English Español
Español Français
Français





