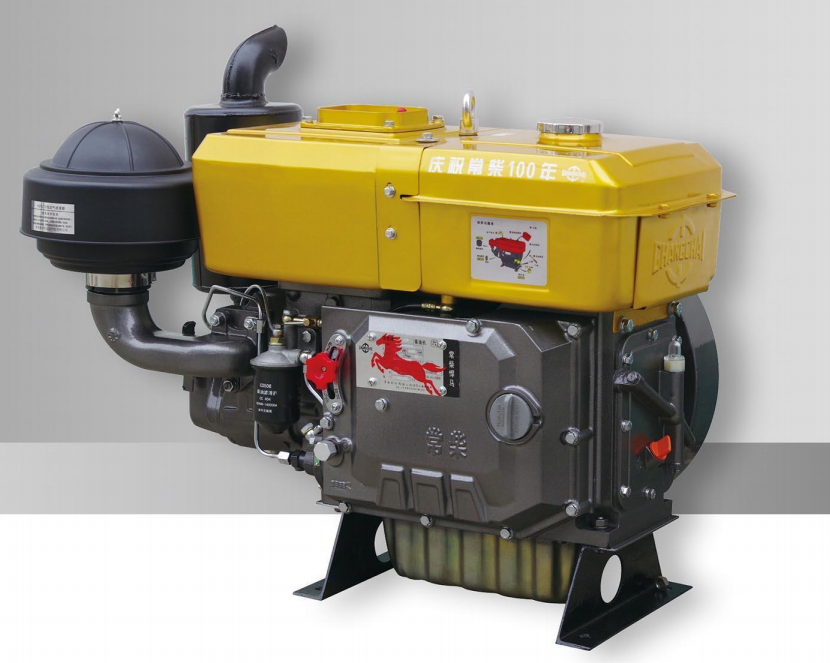
- What is a Multi-Cylinder Engine?
A multi-cylinder engine uses four, six or eight cylinders and is capable of developing a higher output than a single-cylinder engine. The reason for using more cylinders is that a single cylinder can only deliver one power impulse every two crankshaft revolutions.
For this reason, a multi-cylinder engine has more power strokes per revolution than a single cylinder engine and produces smoother torque output. It also has a lower compression ratio and less thermal stress on the reciprocating components due to the smaller cylinder bore.
- Introduction Multi-cylinder Engine
A multi-cylinder engine is a type of internal combustion engine with more than one cylinder. The number of cylinders varies depending on the engine design and the desired displacement of each cylinder.
An example of a multi-cylinder engine is a gas turbine, which uses multiple cylinders to provide more power than a single cylinder. This is typically done to reduce weight or increase speed.
Another type of engine is the radial engine, which has cylinders arranged in a star pattern around a central crankshaft. This is a type of engine that is commonly used in aircraft.
In addition to these traditional engines, there is also the diesel engine, which was invented by Rudolf Diesel. The diesel engine is different from most other types of engines in that the cylinders are not filled with fuel. Instead, the engine uses compression to heat air to a temperature above the auto-ignition temperature of fuel. This allows the engine to achieve higher efficiency than most other engines.
- Multi-cylinder Engine Function
A multi-cylinder engine is designed to provide a greater power stroke per revolution, which makes it more efficient and allows it to run at higher speeds. In a conventional four-stroke engine, each cylinder delivers one power stroke every two crankshaft revolutions and only supplies power for a fourth of the time during the power stroke.
A separate source of compressed air is provided to be connected through valve means to each cylinder. In the case of a piston type internal combustion engine this air is supplied to each cylinder as scavenging or supercharging air.
This air is introduced into each cylinder via ports located adjacent the piston head when the respective pistons are in their bottom dead center position. The air is supplied at a pressure from about 7 to 43 psig, and at a temperature below 1470deg F.
The air may also be sucked in through the connecting ports from a compressor which is driven by the engine crank shaft. This is done for starting and possibly at partial load operation.
- Where are multi-cylinder engines used?
A multi-cylinder engine is a great way to increase the power to weight ratio of a gas powered vehicle. It is also the smartest choice for a number of other uses including powering aircraft and boats.
The best part is that they are inexpensive to build, operate and maintain compared to their single cylinder counterparts. Hence, they are a popular choice amongst enthusiasts and the masses alike.
Despite this, a plethora of smaller, simpler and cheaper options still compete with the multi-cylinder in the quest for performance and efficiency. To help reduce the cost of putting one together, many manufacturers provide a range of kit options for converting your existing car, truck or plane into an all-rounder that is sure to impress the crowd and make you stand out from the rest. A good place to start is your local dealer. They should have no problem recommending the best options available to you. You should also be able to test drive one to see if it is right for you.A multi-cylinder engine is a type of internal combustion engine with more than one cylinder. It has several advantages over a single-cylinder engine.
It produces more power per stroke, and its rpm range is wider, giving it the potential to run faster. It also has more torque output, because of a larger piston-to-cylinder bore ratio.
In addition, a multi-cylinder engine can be adapted to change its displacement through deactivation of some or all of its cylinders. The technology has been around for years and is now widely used in large engines.
A method of operating a multi-cylinder piston type internal combustion engine including introducing into each cylinder scavenging and/or supercharging air when the piston is substantially in its bottom dead center position prior to the beginning of a compression stroke or an exhaust stroke. The quantity of scavenging and/or supercharging is varied in dependence upon the load or output power of the engine.

 中文
中文 English
English Español
Español Français
Français





